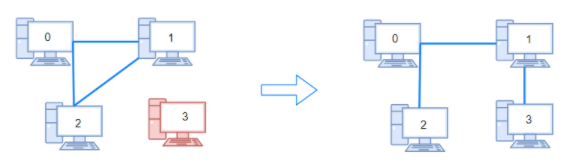
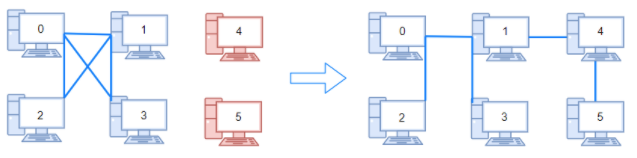
并查集(不相交集合)用于处理 动态连通性 问题,最典型的应用是求解 最小生成树 的 Kruskal 算法;
并查集支持 查询(find)、合并(union) 两个操作;
并查集只回答两个结点是不是在一个连通分量中(也就是所谓的连通性问题),并不回答路径问题。
如果一个问题具有传递性质,可以考虑用并查集;
并查集最常见的一种设计思想是:把同在一个连通分量中的结点组织成一个树形结构(代表元法);
并查集使用 路径压缩 与 按秩合并 解决树的高度增加带来的 查询 性能消耗问题;
可以在《算法(第4版)》第1.5节和《算法导论》第21章中学习并查集。
🔗 给定一个由表示变量之间关系的字符串方程组成的数组,每个字符串方程 equations[i] 的长度为 4,并采用两种不同的形式之一:“a==b” 或 “a!=b”。在这里,a 和 b 是小写字母(不一定不同),表示单字母变量名。
只有当可以将整数分配给变量名,以便满足所有给定的方程时才返回 true,否则返回 false。
示例 1:
输入:[“a==b”,“b!=a”]
示例 2:
输入:["b==a","a==b"]
示例 3:
输入:["a==b","b==c","a==c"]
示例 4:
输入:["a==b","b!=c","c==a"]
示例 5:
输入:["c==c","b==d","x!=z"]
提示:
1 <= equations.length <= 500equations[i].length == 4equations[i][0] 和 equations[i][3] 是小写字母equations[i][1] 要么是 '=',要么是 '!'equations[i][2] 是 '='
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 class Solution public boolean equationsPossible (String[] equations) UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(26 ); for (String equation : equations) { char [] charArray = equation.toCharArray(); if (charArray[1 ] == '=' ) { int idx1 = charArray[0 ] - 'a' ; int idx2 = charArray[3 ] - 'a' ; unionFind.union(idx1, idx2); } } for (String equation : equations) { char [] charArray = equation.toCharArray(); if (charArray[1 ] == '!' ) { int idx1 = charArray[0 ] - 'a' ; int idx2 = charArray[3 ] - 'a' ; if (unionFind.isConnected(idx1, idx2)) { return false ; } } } return true ; } private class UnionFind private int [] parent; public UnionFind (int n) parent = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { parent[i] = i; } } public int find (int x) while (x != parent[x]) { parent[x] = parent[parent[x]]; x = parent[x]; } return x; } public void union (int x, int y) int rootX = find(x); int rootY = find(y); parent[rootX] = rootY; } public boolean isConnected (int x, int y) return find(x) == find(y); } } }
🔗 给你一个变量对数组 equations 和一个实数值数组 values 作为已知条件,其中 equations[i] = [Ai, Bi] 和 values[i] 共同表示等式 Ai / Bi = values[i] 。每个 Ai 或 Bi是一个表示单个变量的字符串。
另有一些以数组 queries 表示的问题,其中 queries[j] = [Cj, Dj] 表示第 j个问题,请你根据已知条件找出 Cj / Dj = ?的结果作为答案。
返回 所有问题的答案 。如果存在某个无法确定的答案,则用 -1.0 替代这个答案。如果问题中出现了给定的已知条件中没有出现的字符串,也需要用 -1.0 替代这个答案。
注意 :输入总是有效的。你可以假设除法运算中不会出现除数为 0 的情况,且不存在任何矛盾的结果。
示例1:
输入:equations = [[“a”,“b”],[“b”,“c”]], values = [2.0,3.0], queries = [[“a”,“c”],[“b”,“a”],[“a”,“e”],[“a”,“a”],[“x”,“x”]]
示例2:
输入:equations = [[“a”,“b”],[“b”,“c”],[“bc”,“cd”]], values = [1.5,2.5,5.0], queries = [[“a”,“c”],[“c”,“b”],[“bc”,“cd”],[“cd”,“bc”]]
示例3:
输入:equations = [[“a”,“b”]], values = [0.5], queries = [[“a”,“b”],[“b”,“a”],[“a”,“c”],[“x”,“y”]]
提示:
1 <= equations.length <= 20
equations[i].length == 2
1 <= Ai.length, Bi.length <= 5
values.length == equations.length
0.0 < values[i] <= 20.0
1 <= queries.length <= 20
queries[i].length == 2
1 <= Cj.length, Dj.length <= 5
Ai, Bi, Cj, Dj 由小写英文字母与数字组成
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 class Solution public double [] calcEquation(List<List<String>> equations, double [] values, List<List<String>> queries) { int equationsSize = equations.size(); UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(2 * equationsSize); Map<String, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<>(2 * equationsSize); int id = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < equationsSize; ++i) { List<String> equation = equations.get(i); String var1 = equation.get(0 ); String var2 = equation.get(1 ); if (!hashMap.containsKey(var1)) { hashMap.put(var1, id); id++; } if (!hashMap.containsKey(var2)) { hashMap.put(var2, id); id++; } unionFind.union(hashMap.get(var1), hashMap.get(var2), values[i]); } int queriesSize = queries.size(); double [] res = new double [queriesSize]; for (int i = 0 ; i <queriesSize; ++i) { String var1 = queries.get(i).get(0 ); String var2 = queries.get(i).get(1 ); Integer id1 = hashMap.get(var1); Integer id2 = hashMap.get(var2); if (id1 == null || id2 == null ) { res[i] = -1.0 ; } else { res[i] = unionFind.isConnected(id1, id2); } } return res; } private class UnionFind private int [] parent; private double [] weight; public UnionFind (int n) this .parent = new int [n]; this .weight = new double [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { parent[i] = i; weight[i] = 1.0d ; } } public void union (int x, int y, double value) int rootX = find(x); int rootY = find(y); if (rootX == rootY) { return ; } parent[rootX] = rootY; weight[rootX] = weight[y] * value / weight[x]; } public int find (int x) if (x != parent[x]) { int origin = parent[x]; parent[x] = find(parent[x]); weight[x] *= weight[origin]; } return parent[x]; } public double isConnected (int x, int y) int rootX = find(x); int rootY = find(y); if (rootX == rootY) { return weight[x] / weight[y]; } else { return -1.0d ; } } } }
🔗 有 n 个城市,其中一些彼此相连,另一些没有相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。
省份 是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有相连的城市。
给你一个 n x n 的矩阵 isConnected ,其中 isConnected[i][j] = 1 表示第 i 个城市和第 j 个城市直接相连,而 isConnected[i][j] = 0 表示二者不直接相连。
返回矩阵中 省份 的数量。
示例 1:
输入:isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]]
示例 2:
输入:isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]
提示:
1 <= n <= 200n == isConnected.lengthn == isConnected[i].lengthisConnected[i][j] 为 1 或 0isConnected[i][i] == 1isConnected[i][j] == isConnected[j][i]
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 class Solution public int findCircleNum (int [][] isConnected) if (isConnected.length <= 1 ) { return isConnected.length; } int n = isConnected.length; UF uf = new UF(n); for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { for (int j = i + 1 ; j < n; ++j) { if (isConnected[i][j] == 1 ) { uf.union(i, j); } } } return uf.count(); } private class UF private int [] id; public UF (int n) id = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { id[i] = i; } } public int count () int cnt = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < id.length; ++i){ if (id[i] == i) { cnt++; } } return cnt; } public void union (int p, int q) int rootP = find(p); int rootQ = find(q); if (rootP != rootQ) { id[rootP] = rootQ; } } public int find (int x) if (id[x] == x) { return x; } return id[x] = find(id[x]); } } }
🔗 树可以看成是一个连通且 无环 的 无向 图。
给定往一棵 n 个节点 (节点值 1~n) 的树中添加一条边后的图。添加的边的两个顶点包含在 1 到 n 中间,且这条附加的边不属于树中已存在的边。图的信息记录于长度为 n 的二维数组 edges ,edges[i] = [ai, bi] 表示图中在 ai 和 bi 之间存在一条边。
请找出一条可以删去的边,删除后可使得剩余部分是一个有着 n 个节点的树。如果有多个答案,则返回数组 edges 中最后出现的边。
示例 1:
输入: edges = [[1,2], [1,3], [2,3]]
示例 2:
输入: edges = [[1,2], [2,3], [3,4], [1,4], [1,5]]
提示:
n == edges.length
3 <= n <= 1000
edges[i].length == 2
1 <= ai < bi <= edges.length
ai != bi
edges 中无重复元素
给定的图是连通的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 package leetcode.unionfind;public class RedundantConnection684 public int [] findRedundantConnection(int [][] edges) { int [] res = new int [2 ]; UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(edges.length); for (int i = 0 ; i < edges.length; ++i) { if (unionFind.isConnented(edges[i][0 ] - 1 , edges[i][1 ] - 1 )) { res[0 ] = edges[i][0 ]; res[1 ] = edges[i][1 ]; } else { unionFind.union(edges[i][0 ] - 1 , edges[i][1 ] - 1 ); } } return res; } private class UnionFind private int [] parent; public UnionFind (int n) parent = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { parent[i] = i; } } void union (int x, int y) int rootX = find(x); int rootY = find(y); parent[rootY] = rootX; } int find (int x) if (parent[x] == x) { return x; } return parent[x] = find(parent[x]); } boolean isConnented (int x, int y) return find(x) == find(y); } } }
🔗 用以太网线缆将 n 台计算机连接成一个网络,计算机的编号从 0 到 n-1。线缆用 connections 表示,其中 connections[i] = [a, b] 连接了计算机 a 和 b。
网络中的任何一台计算机都可以通过网络直接或者间接访问同一个网络中其他任意一台计算机。
给你这个计算机网络的初始布线 connections,你可以拔开任意两台直连计算机之间的线缆,并用它连接一对未直连的计算机。请你计算并返回使所有计算机都连通所需的最少操作次数。如果不可能,则返回 -1 。
示例1:
输入:n = 4, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,2]]
示例2:
输入:n = 6, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,2],[1,3]]
示例 3:
输入:n = 6, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,2]]
示例 4:
输入:n = 5, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[3,4],[2,3]]
提示:
1 <= n <= 10^51 <= connections.length <= min(n*(n-1)/2, 10^5)connections[i].length == 20 <= connections[i][0], connections[i][1] < nconnections[i][0] != connections[i][1]没有重复的连接。
两台计算机不会通过多条线缆连接。
需要维护一个变量表示当前连通分量的个数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 class Solution public int makeConnected (int n, int [][] connections) if (connections.length < n - 1 ) { return -1 ; } UnionFind unionFind = new UnionFind(n); for (int [] conn : connections) { if (!unionFind.isConnented(conn[0 ], conn[1 ])) { unionFind.union(conn[0 ], conn[1 ]); } } return unionFind.setCnt - 1 ; } private class UnionFind int [] parent; int setCnt; public UnionFind (int n) setCnt = n; parent = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { parent[i] = i; } } void union (int x, int y) int rootX = find(x); int rootY = find(y); parent[rootY] = rootX; --setCnt; } int find (int x) if (parent[x] == x) { return x; } return parent[x] = find(parent[x]); } boolean isConnented (int x, int y) return find(x) == find(y); } } }
🔗 你准备参加一场远足活动。给你一个二维 rows x columns 的地图 heights ,其中 heights[row][col] 表示格子 (row, col) 的高度。一开始你在最左上角的格子 (0, 0) ,且你希望去最右下角的格子 (rows-1, columns-1) (注意下标从 0 开始编号)。你每次可以往 上,下,左,右 四个方向之一移动,你想要找到耗费 体力 最小的一条路径。
一条路径耗费的 体力值 是路径上相邻格子之间 高度差绝对值 的 最大值 决定的。
请你返回从左上角走到右下角的最小 体力消耗值 。
示例1:
输入:heights = [[1,2,2],[3,8,2],[5,3,5]]
示例2:
输入:heights = [[1,2,3],[3,8,4],[5,3,5]]
示例3:
输入:heights = [[1,2,1,1,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,2,1,2,1],[1,1,1,2,1]]
提示:
rows == heights.lengthcolumns == heights[i].length1 <= rows, columns <= 1001 <= heights[i][j] <= 10^6
用并查集算法解决该问题的关键是要建立图的模型,根据走的方向来建立不同坐标之间的连通关系,然后需要根据权值从小到大排序,才能在首次检测到起点与终点连通的时候,是最低的体力消耗。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 public class MinimumEffortPath1631 public int minimumEffortPath (int [][] heights) int m = heights.length; int n = heights[0 ].length; List<int []> edges = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0 ; i < m; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < n; ++j) { int id = i * n + j; if (i > 0 ) { edges.add(new int []{id - n, id, Math.abs(heights[i][j] - heights[i - 1 ][j])}); } if (j > 0 ) { edges.add(new int []{id - 1 , id, Math.abs(heights[i][j] - heights[i][j - 1 ])}); } } } Collections.sort(edges, new Comparator<int []>() { public int compare (int [] edge1, int [] edge2) return edge1[2 ] - edge2[2 ]; } }); UnionFind uf = new UnionFind(m * n); int ans = 0 ; for (int [] edge : edges) { int x = edge[0 ], y = edge[1 ], v = edge[2 ]; uf.union(x, y); if (uf.isConnented(0 , m * n - 1 )) { ans = v; break ; } } return ans; } private class UnionFind private int [] parent; public UnionFind (int n) parent = new int [n]; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; ++i) { parent[i] = i; } } void union (int x, int y) int rootX = find(x); int rootY = find(y); parent[rootY] = rootX; } int find (int x) if (parent[x] == x) { return x; } return parent[x] = find(parent[x]); } boolean isConnented (int x, int y) return find(x) == find(y); } } }