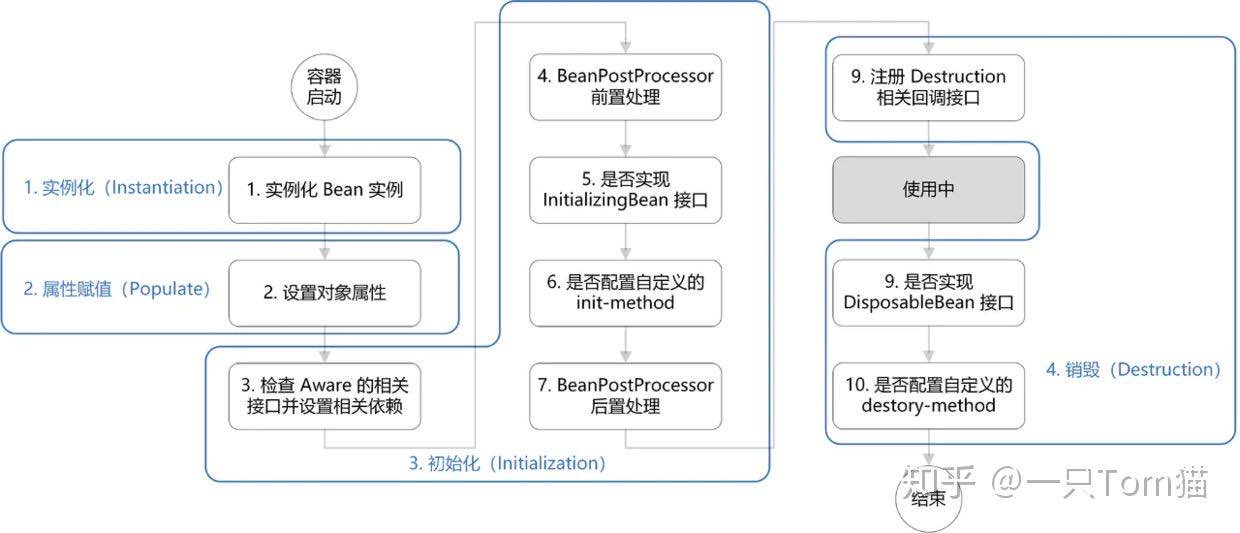
Spring Bean生命周期
Bean 的生命周期概括起来就是 4 个阶段:
- 实例化(Instantiation)
- 属性赋值(Populate)
- 初始化(Initialization)
- 销毁(Destruction)
![bean生命周期]()
- 实例化:第 1 步,实例化一个 bean 对象;
- 属性赋值:第 2 步,为 bean 设置相关属性和依赖;
- 初始化:第 3~7 步,步骤较多,其中第 5、6 步为初始化操作,第 3、4 步为在初始化前执行,第 7 步在初始化后执行,该阶段结束,才能被用户使用;
- 销毁:第 8~10步,第8步不是真正意义上的销毁(还没使用呢),而是先在使用前注册了销毁的相关调用接口,为了后面第9、10步真正销毁 bean 时再执行相应的方法。
深入源码
下面我们结合代码来直观的看下,在 doCreateBean() 方法中能看到依次执行了这 4 个阶段:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
return exposedObject;
}
|
由于初始化包含了第 3~7步,较复杂,所以我们进到initializeBean() 方法里具体看下其过程(注释的序号对应图中序号):
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
|
在 invokInitMethods() 方法中会检查 InitializingBean 接口和 init-method 方法,销毁的过程也与其类似:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public void destroy() {
if (this.invokeDisposableBean) {
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {
((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy();
return null;
}, this.acc);
}
else {
((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy();
}
}
}
if (this.destroyMethod != null) {
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod);
}
else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) {
Method methodToInvoke = determineDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethodName);
if (methodToInvoke != null) {
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(ClassUtils.getInterfaceMethodIfPossible(methodToInvoke));
}
}
}
|
从 Spring 的源码我们可以直观的看到其执行过程,而我们记忆其过程便可以从这 4 个阶段出发,实例化、属性赋值、初始化、销毁。其中细节较多的便是初始化,涉及了 Aware、BeanPostProcessor、InitializingBean、init-method 的概念。
扩展点的作用
Aware接口
若 Spring 检测到 bean 实现了 Aware 接口,则会为其注入相应的依赖。所以通过让bean 实现 Aware 接口,则能在 bean 中获得相应的 Spring 容器资源。
Spring 中提供的 Aware 接口有:
BeanNameAware:注入当前 bean 对应 beanName;BeanClassLoaderAware:注入加载当前 bean 的 ClassLoader;BeanFactoryAware:注入 当前BeanFactory容器 的引用。
以上是针对 BeanFactory 类型的容器,而对于 ApplicationContext 类型的容器,也提供了 Aware 接口,只不过这些 Aware 接口的注入实现,是通过 BeanPostProcessor 的方式注入的,但其作用仍是注入依赖。
EnvironmentAware:注入 Enviroment,一般用于获取配置属性;EmbeddedValueResolverAware:注入 EmbeddedValueResolver(Spring EL解析器),一般用于参数解析;ApplicationContextAware(ResourceLoader、ApplicationEventPublisherAware、MessageSourceAware):注入 ApplicationContext 容器本身。
BeanPostProcessor
BeanPostProcessor是 Spring 为修改 bean提供的强大扩展点,其可作用于容器中所有 bean,其定义如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| public interface BeanPostProcessor {
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
}
|
常用场景有:
- 对于标记接口的实现类,进行自定义处理。例如上面Aware接口所说的ApplicationContextAwareProcessor,为其注入相应依赖;再举个例子,自定义对实现解密接口的类,将对其属性进行解密处理;
- 为当前对象提供代理实现。例如 Spring AOP 功能,生成对象的代理类,然后返回。
InitializingBean 和init-method
InitializingBean 和init-method是 Spring 为 bean 初始化提供的扩展点。
InitializingBean接口的定义如下:
1
2
3
| public interface InitializingBean {
void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception;
}
|
指定 init-method 方法,指定初始化方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="demo" class="com.chaycao.Demo" init-method="init()"/>
</beans>
|
DisposableBean 和 destory-method 与上述类似,就不描述了。